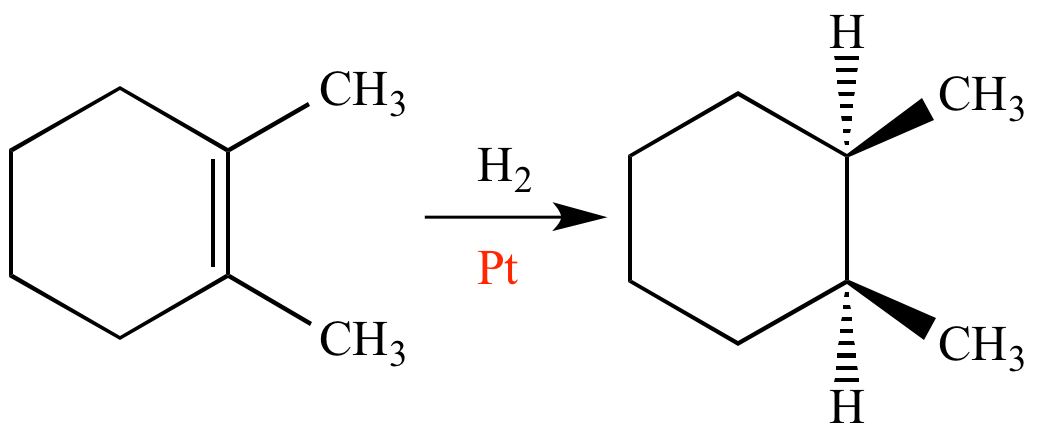What Is Catalyst In Chemistry
Find, Read, And Discover What Is Catalyst In Chemistry, Such Us:
- Ir Catalyst Attacks Strong C H Bonds Without Directing Group What Is Catalyst In Chemistry,
- Catalysis And Sustainable Green Chemistry Sciencedirect What Is Catalyst In Chemistry,
- Chem Rate Of Reaction Chemistry Rate Of Reaction Catalyst What Is Catalyst In Chemistry,
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcsiktytopxjq0wmci7krxg3icl3ns8jxeldsckevgtcr Wnvklc Usqp Cau What Is Catalyst In Chemistry,
- How To Identify The Intermediate Catalyst In A Reaction Mechanism Kinetics Chemistry Youtube What Is Catalyst In Chemistry,
What Is Catalyst In Chemistry, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
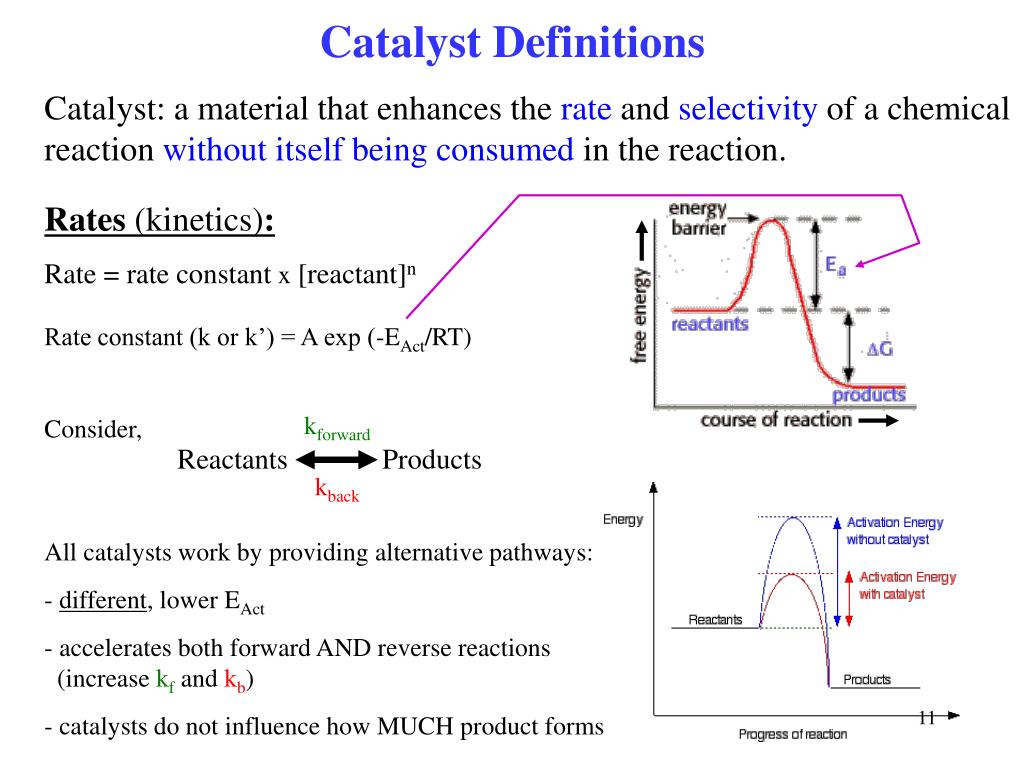
Ppt Heterogeneous Catalysis 6 Lectures Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 809783 What Is Cat Virus
Hence a catalyst can be recovered chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction it has been used to speed up or catalyze.
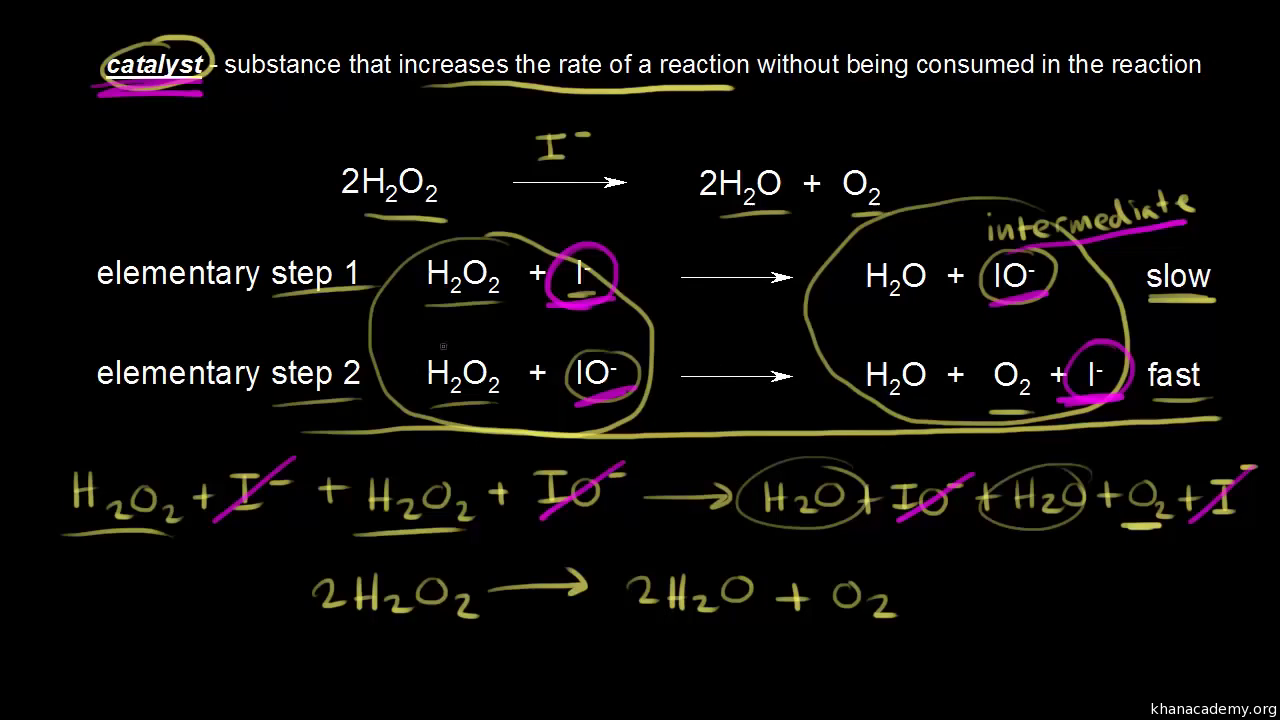
What is cat virus. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not consumed during the course of the reaction. Catalysis k e t ae l e s s is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst k ae t el s t catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction but can act repeatedly. Catalysts are the unsung heroes of the chemical reactions that make human society tick.
Catalysis is defined as increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by introducing a catalysta catalyst in turn is a substance that is not consumed by the chemical reaction but acts to lower its activation energyin other words a catalyst is both a reactant and product of a chemical reaction. Typically only a very small quantity of catalyst is required in order to catalyze a reaction. A catalyst therefore does not appear in the overall stoichiometry of the reaction it catalyzes but it must appear in at least one of the elementary reactions in the mechanism for the catalyzed reaction.
For example a catalyst could cause a reaction between reactants to happen at a faster rate or at a lower temperature than would be possible without the catalyst. Catalyst definition is a substance that enables a chemical reaction to proceed at a usually faster rate or under different conditions as at a lower temperature than otherwise possible. With a helping hand from a catalyst molecules that might take years to interact can now do so in seconds.
A catalyst will appear in the steps of a reaction mechanism but it will not appear in the overall chemical reaction as it is not a reactant or product. A catalyst is some material that speeds up chemical reactions. Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process.
Often only very small amounts of catalyst are required. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but is not consumed by the reaction. A chemical catalyst is a substance that causes a chemical reaction to happen in a different way than it would happen without that catalyst.
The global demand for catalysts in 2010 was estimated at approximately us295 billion. Catalyst in chemistry any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed. Factories rely on catalysts to make everything from plastic to drugs.
In general catalytic action is a chemical reaction between the catalyst and a reactant. Catalysis in chemistry the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction usually an acceleration by addition of a substance not consumed during the reactionthe rates of chemical reactionsthat is the velocities at which they occurdepend upon a number of factors including the chemical nature of the reacting species and the external conditions to which they are exposed.
More From What Is Cat Virus
- Dog Eat Dog All Boro Kings Vinyl
- Doja Cat Old Song About Drugs
- Black Cat Race
- Ozuna Feat Doja Cat Sia Del Mar
- Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia
Incoming Search Terms:
- Ir Catalyst Attacks Strong C H Bonds Without Directing Group Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia,
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcsiktytopxjq0wmci7krxg3icl3ns8jxeldsckevgtcr Wnvklc Usqp Cau Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia,
- Homogeneous Gold Redox Chemistry Organometallics Catalysis And Beyond Trends In Chemistry Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia,
- Chemistry With N Centered Radicals Generated By Single Electron Transfer Oxidation Using Photoredox Catalysis Ccs Chemistry Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia,
- An Overview Of Different Types Of Catalysts Legal Advantage Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia,
- How To Identify The Intermediate Catalyst In A Reaction Mechanism Kinetics Chemistry Youtube Cat Dog Bahasa Indonesia,