What Is Catalyst In Biology
Find, Read, And Discover What Is Catalyst In Biology, Such Us:
- Biological Catalysts Enzymes Igcse Biology Ppt Download What Is Catalyst In Biology,
- What Are Catalysts Reactions Chemistry Fuseschool Youtube What Is Catalyst In Biology,
- Catalyst What Is Catalyst In Biology,
- Enzymes Biology Libretexts What Is Catalyst In Biology,
- Alphabetic Life And Its Inevitability Biopolyverse What Is Catalyst In Biology,
What Is Catalyst In Biology, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
Enzymes speed up rate of reaction inside the body.
Black cat kidnapped. Enzymes are naturally occurring catalysts responsible for many essential biochemical reactions. Catalysts in the largest biology dictionary online. Enzymes are important because they allow cells.
A substance as an enzyme that enables a chemical reaction to proceed at a usually faster rate or under different conditions as at a lower temperature than otherwise possible. Catalyst definition a substance that causes or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected. Catalyst in chemistry any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed.
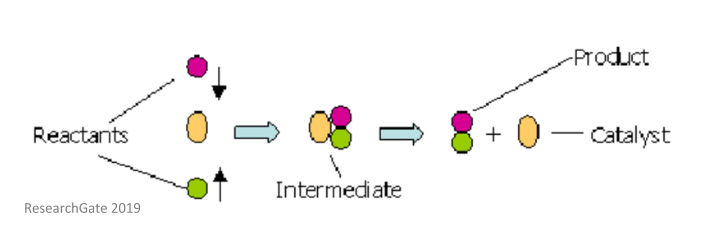
These reactions include respiration photosynthesis and making new proteins. Definition noun plural catalyst a substance capable of initiating or speeding up a chemical reaction. A biological catalyst is an enzyme.
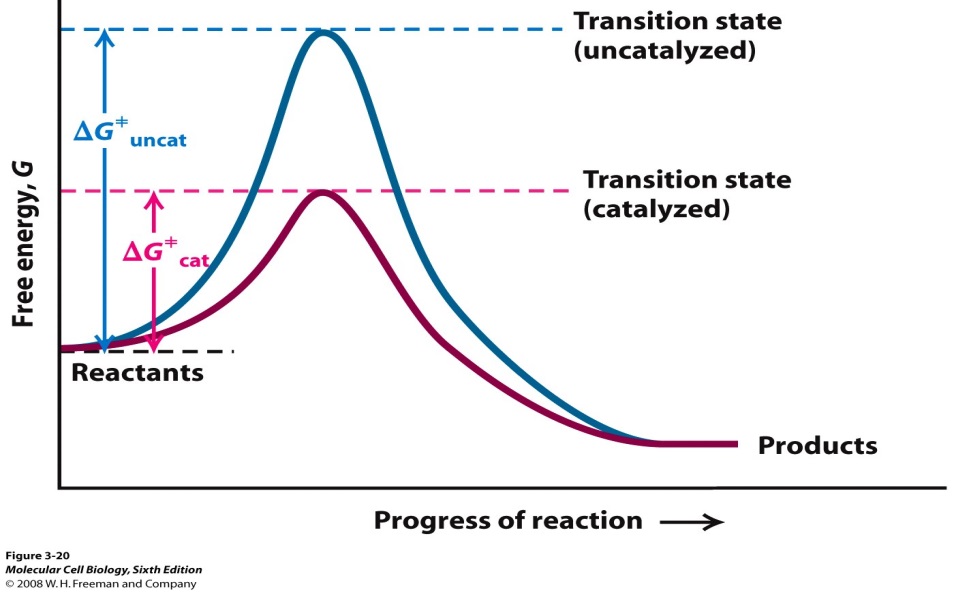
The presence of a catalyst can make chemical reactions proceed faster by a factor of several million times. The catalyst may be chemically transformed but only transiently during the reaction. In biology a catalyst is a substance which speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed themselves.
Catalyst a substance that helps a chemical reaction to proceed faster. Biological catalysts are found in living organisms. Examples include enzymes and elements such as platinum and iridium.
In general catalytic action is a chemical reaction between the catalyst and a reactant. Medical definition of catalyst. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions inside cells.
Catalyst in biology is enzyme. Examples include enzymes and elements such as platinum and iridium. Enzymes are soluble protein molecules that can speed up chemical reactions in cells.
Supplement chemical reaction can proceed spontaneously even without a catalyst but it would be too slow.
More From Black Cat Kidnapped
- Cat Dog Dataset Download
- Doja Cat Cow Shirt
- Youtube Doja Cat Moo
- Cats Eye Stone
- Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer
Incoming Search Terms:
- Catalyst Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer,
- 1 4 Rate Of Reaction 1 2d Biology Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer,
- Biol2060 Cell Biology Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer,
- Biology 2 4 Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer,
- Catalysis Wikipedia Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer,
- Effect Of Catalysts Doja Cat Mother Deborah Elizabeth Sawyer,